Better hearing starts with understanding.
Hearing loss in Australia.
About 3.6 million people have some degree of hearing loss in Australia
Hearing loss affects about 1 in 6 Australians.
This is expected to rise to 1 in 4 Australians by 2050.
Over half the population aged between 60 and 70 have hearing loss.
This increases to more than 70% of those over the age of 70 and 80% of those over the age of 80.
Types of Hearing loss
Hearing loss affects people of all ages and can be caused by many different factors. The three basic categories of hearing loss are sensorineural, conductive, and mixed hearing loss.
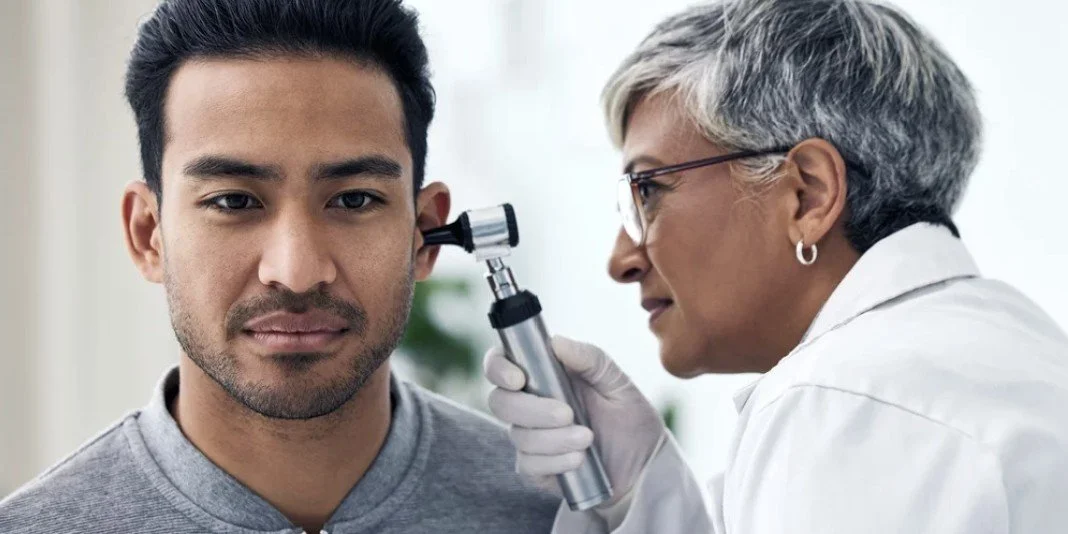
As there are different types of hearing loss, it’s important to have a comprehensive diagnostic hearing assessment. As with any medical condition, it’s best to know what you have before deciding on what to do about it. A consultation with an Audiologist can help to determine the type, cause and degree of your hearing loss.
Sensorineural Hearing loss
This type of hearing loss occurs when the inner ear or the actual hearing nerve itself becomes damaged. This loss generally occurs when some of the hair cells within the cochlea are damaged.
Sensorineural loss is the most common type of hearing loss. It can be a result of aging, exposure to loud noise/music, injury, disease, certain drugs or an inherited condition. This type of hearing loss is typically not medically or surgically treatable. However, many people with this type of loss find that hearing aids can be beneficial.
Causes of Sensorineural hearing loss
Sudden sensorineural
hearing loss
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss may occur very suddenly or over the course of a few days. Mostly, the hearing loss is noticed in one ear. Sometimes people wake up with hearing loss. It may be conductive or sensorineural. This is an emergency.
It is imperative to see an Audiologist/Otologist (a doctor specializing in diseases of the ear) immediately. A delay in treating this condition (two or more weeks after the symptoms first begin) will decrease the chance that medications might help to improve the problem.
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss can be caused by many things. These include infection, sudden pressure change (eg. deep water diving), stroke, head injury, medicines or other health conditions. In most cases, no cause is found. You might also have tinnitus, dizziness, nausea and vomiting and your ear may feel full or blocked.
If you are treated quickly, you will have a better chance of recovery. If no cause is found, you might be prescribed a steroid medicine, which can help your hearing recover. In some people, hearing loss will be permanent. You require periodical hearing assessments to monitor the changes in your ear and hearing.
Conductive Hearing Loss
This type of hearing loss occurs in the outer or middle ear where sound waves are not able to carry all the way through to the inner ear. Sound may be blocked by earwax, or a foreign object located in the ear canal. The middle ear space may be impacted with fluid, infection, or a bone abnormality; or the eardrum may have been injured.
In some people, conductive hearing loss may be reversed through medical or surgical intervention. Conductive hearing loss is most common in children who may have recurrent ear infections or who insert foreign objects into their ear canal.
Causes of conductive hearing loss
Infections of the ear canal or middle ear resulting in fluid or pus buildup.
Perforation or scarring of the eardrum.
Wax buildup
Dislocation of the middle ear bones (ossicles).
Foreign object in the ear canal.
Otosclerosis (an abnormal bone growth in the middle ear).
Abnormal growths or tumours.
Early Signs of Hearing Loss
Having trouble hearing in noisy places.
Having trouble hearing people on the phone or if they’re not facing you.
Often asking people to repeat themselves.
Hearing sounds as muffled, as though people are mumbling.
Needing to have the TV / radio up louder than other people.
Often missing your phone or the doorbell ringing.Hearing buzzing or ringing in your ears.
Avoiding social situations because you have trouble hearing.
Accused of having selective hearing.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is just what it sounds like a combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.
Benefits of Treating Hearing loss
Reduces the risk of memory problems/dementia.
Communication and engaging in conversation are easier.
Improves cognitive function.
Long and healthy ageing.
Improved safety and balance.
Improved relationships.
Improves confidence and independence.
Better mental health (emotional and social)
Enhanced overall health and wellbeing.